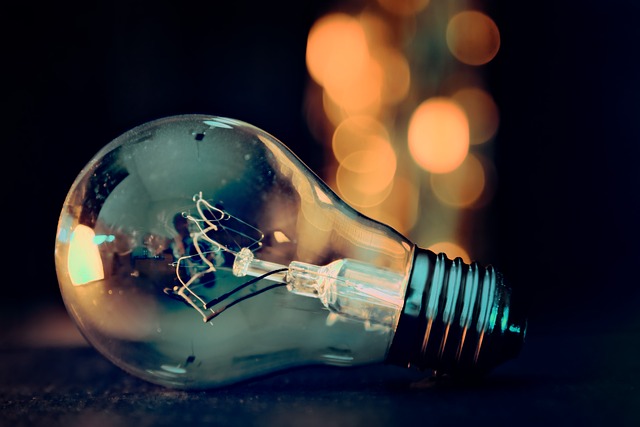

The Incandescent Light Bulb
The incandescent light bulb has been a staple in homes and businesses for over a century. Known for its warm glow and simplicity, this type of lighting has played a significant role in transforming how we illuminate our spaces. Let’s dive into what makes incandescent bulbs tick, their advantages, and some considerations to keep in mind.
How Incandescent Bulbs Work
At the heart of an incandescent bulb is a filament, usually made of tungsten. When electricity passes through this filament, it heats up due to a process called Joule heating, eventually glowing and producing light. This process occurs within a glass bulb that is either vacuum-sealed or filled with inert gas to prevent oxidation, ensuring the filament lasts as long as possible.
Types and Sizes
Incandescent bulbs come in a variety of sizes and voltage ratings, ranging from 1.5 volts to about 300 volts. This versatility allows them to be used in various applications, from household lighting to portable lamps and even car headlights. Their straightforward design means they don’t require any external regulating equipment, making them easy to use in almost any setting.
Advantages of Incandescent Bulbs
- Warm Light Quality: Many people appreciate the soft, warm light that incandescent bulbs provide, which can create a cozy atmosphere in any room. 🌟
- Instant Brightness: Unlike some other types of bulbs, incandescent lights turn on at full brightness immediately, making them convenient for quick lighting needs.
- Low Initial Cost: They are generally inexpensive to purchase, which can be appealing for those looking to save on upfront costs.
- Compatibility: Incandescent bulbs work well with both alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC), providing flexibility in different electrical setups.
Considerations
While incandescent bulbs have their perks, there are some important factors to consider:
- Shorter Lifespan: Typically, incandescent bulbs last around 1,000 hours, which is significantly shorter than compact fluorescent bulbs (around 10,000 hours) or LED bulbs (up to 25,000 hours).
- Energy Efficiency: Incandescent bulbs are less energy-efficient compared to newer technologies. They convert a lot of energy into heat rather than light, which can lead to higher electricity bills over time.
- Environmental Impact: With their shorter lifespan and higher energy consumption, incandescent bulbs can have a larger environmental footprint compared to more efficient lighting options.
Conclusion
In summary, incandescent light bulbs offer a classic lighting solution with their warm glow and simplicity. However, as energy efficiency becomes increasingly important, many are turning to alternatives like LED and CFL bulbs. Understanding the pros and cons of incandescent lighting can help make informed choices about how to light your home or workspace. 💡
















 Unpacking Princess Luna's Cutie Mark: A Royal Mystery!
Unpacking Princess Luna's Cutie Mark: A Royal Mystery! 
 Health
Health  Fitness
Fitness  Lifestyle
Lifestyle  Tech
Tech  Travel
Travel  Food
Food  Education
Education  Parenting
Parenting  Career & Work
Career & Work  Hobbies
Hobbies  Wellness
Wellness  Beauty
Beauty  Cars
Cars  Art
Art  Science
Science  Culture
Culture  Books
Books  Music
Music  Movies
Movies  Gaming
Gaming  Sports
Sports  Nature
Nature  Home & Garden
Home & Garden  Business & Finance
Business & Finance  Relationships
Relationships  Pets
Pets  Shopping
Shopping  Mindset & Inspiration
Mindset & Inspiration  Environment
Environment  Gadgets
Gadgets  Politics
Politics 