Microscope Labeled
Understanding the Microscope
The microscope is an essential tool in the field of science, particularly in biology and materials science. It allows users to observe objects that are too small to be seen with the naked eye. Understanding the various parts of a microscope and their functions is crucial for effective use. This article provides a detailed overview of the labeled parts of a microscope.
Parts of a Microscope
A typical microscope consists of several key components, each serving a specific purpose. Below is a breakdown of these parts:
- Eyepiece (Ocular Lens): The lens at the top of the microscope that the user looks through. It typically has a magnification of 10x or 15x.
- Objective Lenses: These are located on the rotating nosepiece and come in various magnifications (e.g., 4x, 10x, 40x, 100x). They are responsible for the initial magnification of the specimen.
- Nosepiece: The rotating part that holds the objective lenses. It allows the user to switch between different magnifications easily.
- Stage: The flat platform where the slide is placed. It often has clips to hold the slide in place.
- Stage Controls: These knobs allow the user to move the stage up and down or side to side for precise positioning of the slide.
- Illuminator: A light source, usually located at the base of the microscope, that illuminates the specimen for better visibility.
- Diaphragm: A disk located under the stage that controls the amount of light reaching the specimen. Adjusting it can enhance contrast and clarity.
- Condenser: A lens system located under the stage that focuses light onto the specimen, improving image quality.
- Base: The bottom part of the microscope that provides stability and support.
- Arm: The part of the microscope that connects the base to the head and provides a handle for carrying the microscope.
Functionality of Each Part
Each component of the microscope plays a vital role in the overall functionality:
- Eyepiece: Magnifies the image further and allows the user to view the specimen comfortably.
- Objective Lenses: Provide different levels of magnification, allowing for detailed examination of the specimen.
- Nosepiece: Facilitates easy switching between lenses without needing to remove the slide.
- Stage: Holds the specimen securely while allowing for adjustments in position.
- Illuminator: Ensures that the specimen is well-lit, which is essential for clear observation.
- Diaphragm: Helps control light intensity, which can affect the visibility of the specimen.
- Condenser: Focuses light onto the specimen, enhancing the clarity and detail of the image.
- Base: Provides a sturdy foundation, essential for maintaining the microscope's stability during use.
- Arm: Offers a safe way to transport the microscope without risking damage to its delicate components.
Conclusion
Understanding the labeled parts of a microscope is fundamental for anyone interested in scientific exploration. Whether used in a classroom or a laboratory, knowing how to operate a microscope effectively can greatly enhance the learning experience. With this knowledge, users can delve deeper into the microscopic world, making discoveries that contribute to various fields of study.
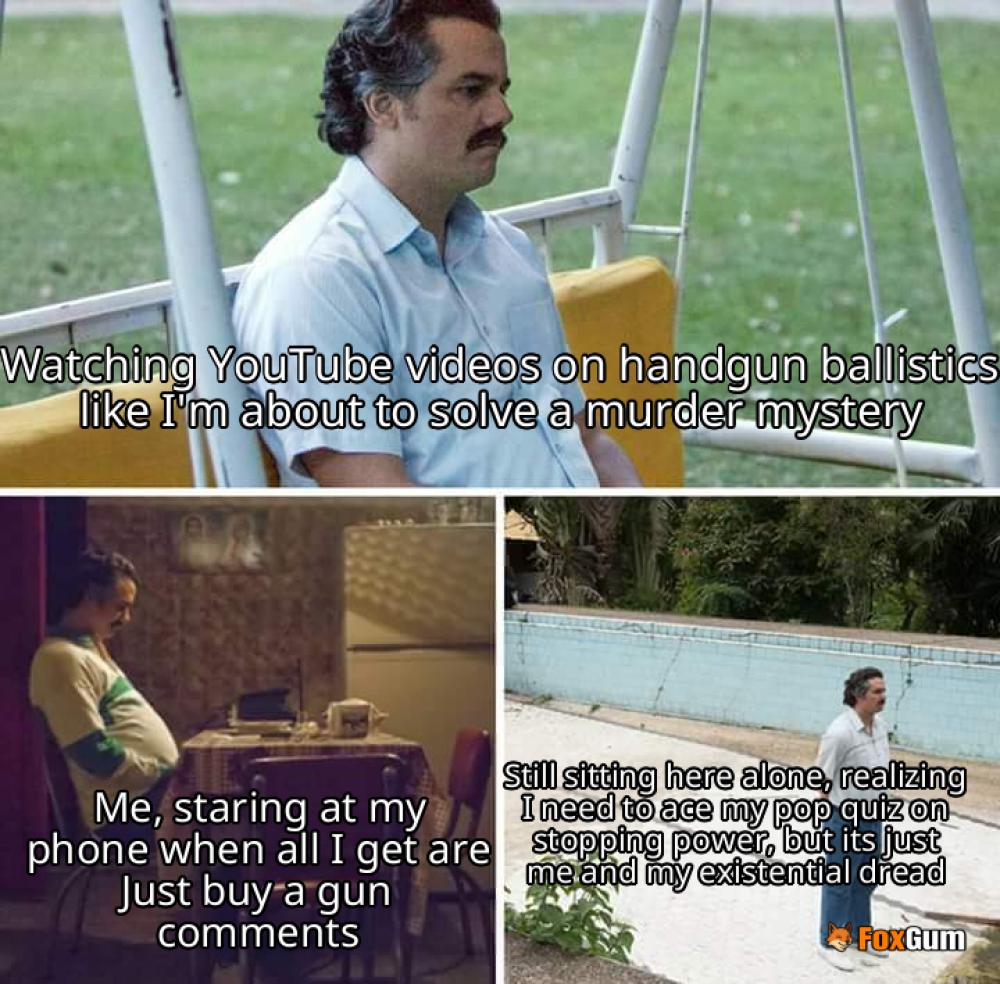

















 Handgun Ballistics Comparison Stopping Power
Handgun Ballistics Comparison Stopping Power 
 Health
Health  Fitness
Fitness  Lifestyle
Lifestyle  Tech
Tech  Travel
Travel  Food
Food  Education
Education  Parenting
Parenting  Career & Work
Career & Work  Hobbies
Hobbies  Wellness
Wellness  Beauty
Beauty  Cars
Cars  Art
Art  Science
Science  Culture
Culture  Books
Books  Music
Music  Movies
Movies  Gaming
Gaming  Sports
Sports  Nature
Nature  Home & Garden
Home & Garden  Business & Finance
Business & Finance  Relationships
Relationships  Pets
Pets  Shopping
Shopping  Mindset & Inspiration
Mindset & Inspiration  Environment
Environment  Gadgets
Gadgets  Politics
Politics 