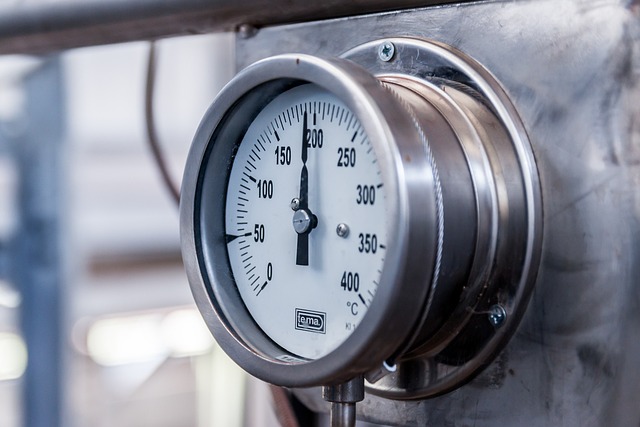

Respiratory Mechanics in Mechanically Ventilated Patients
Understanding Respiratory Mechanics
Respiratory mechanics is a crucial aspect of managing patients who are mechanically ventilated. It encompasses the study of lung function through various measures of pressure and flow. By analyzing these metrics, healthcare professionals can derive important indices that help in assessing and optimizing ventilation strategies. This article delves into the fundamental concepts of respiratory mechanics and their significance in the context of mechanical ventilation.
The Basics of Pressure and Flow
At the core of respiratory mechanics are two primary components: pressure and flow. These elements allow clinicians to evaluate how effectively a patient’s lungs are functioning under mechanical support. Key measurements include:
- Plateau Pressure: This measures the end-inspiratory distending pressure in the lungs and is essential for assessing lung compliance.
- Compliance: This refers to the ability of the lungs to expand and contract. High compliance indicates easier lung expansion, while low compliance can signal potential issues.
- Resistance: This measures the opposition to airflow within the airways. Increased resistance can complicate ventilation and may require adjustments in therapy.
- Work of Breathing: This indicates the effort required to breathe and can provide insights into a patient’s respiratory status.
The Role of Esophageal Manometry
One area gaining attention in respiratory mechanics is esophageal manometry. This technique measures pressures in the esophagus, which can provide valuable information about intrathoracic pressures and lung mechanics. In mechanically ventilated patients, understanding these pressures can help guide the adjustment of ventilator settings, particularly in determining optimal levels of positive end-expiratory pressure (PEEP).
Stress and Strain in Mechanical Ventilation
Another important concept in respiratory mechanics is the assessment of stress and strain on lung tissues during mechanical ventilation. The stress index, derived from the shape of the pressure-time curve, can help clinicians evaluate the potential for lung injury. Monitoring these factors is vital to ensure that ventilation strategies do not inadvertently cause harm to the lungs.
Guiding PEEP Settings
PEEP is a critical parameter in mechanical ventilation that helps prevent alveolar collapse at the end of expiration. By using measures such as end-expiratory transpulmonary pressure and the stress index, healthcare providers can tailor PEEP settings to optimize lung function while minimizing the risk of injury. This personalized approach can lead to better outcomes for patients requiring mechanical support.
Conclusion
Understanding respiratory mechanics is essential for effective management of mechanically ventilated patients. By focusing on pressure and flow measurements, as well as employing techniques like esophageal manometry, healthcare professionals can enhance ventilation strategies and improve patient care. As research continues to evolve in this field, the insights gained will undoubtedly lead to more refined approaches in the treatment of respiratory failure.
















 The Role of an Oncology Nurse
The Role of an Oncology Nurse 
 Health
Health  Fitness
Fitness  Lifestyle
Lifestyle  Tech
Tech  Travel
Travel  Food
Food  Education
Education  Parenting
Parenting  Career & Work
Career & Work  Hobbies
Hobbies  Wellness
Wellness  Beauty
Beauty  Cars
Cars  Art
Art  Science
Science  Culture
Culture  Books
Books  Music
Music  Movies
Movies  Gaming
Gaming  Sports
Sports  Nature
Nature  Home & Garden
Home & Garden  Business & Finance
Business & Finance  Relationships
Relationships  Pets
Pets  Shopping
Shopping  Mindset & Inspiration
Mindset & Inspiration  Environment
Environment  Gadgets
Gadgets  Politics
Politics 