
Burrowing Spiders
Introduction to Burrowing Spiders
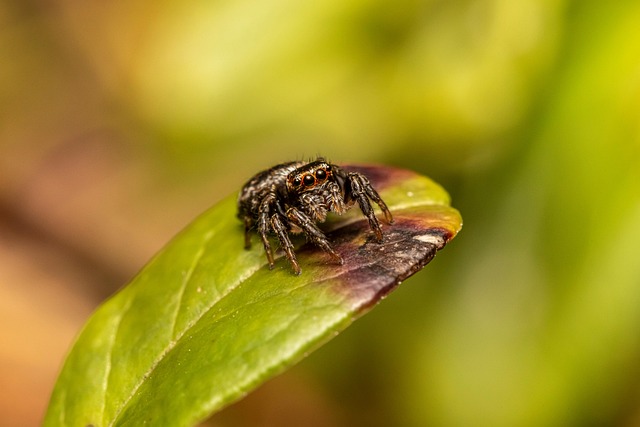
Burrowing spiders, particularly those in the genus Geolycosa, are fascinating creatures that have adapted to a unique lifestyle. These spiders are known for their distinctive burrowing behavior, which sets them apart from many other spider species. This article will explore their characteristics, habitat, and behavior, providing a comprehensive overview of these intriguing arachnids.
Characteristics of Burrowing Spiders
Burrowing spiders are typically robust and well-adapted for life underground. They possess strong legs that enable them to dig and navigate their burrows effectively. One of the most notable features of these spiders is their chelicerae, which are powerful jaws tipped with fangs. These are essential for capturing and consuming prey.
In addition to their chelicerae, burrowing spiders have a pair of palps, which resemble short legs. These appendages are used to manipulate food and assist in various tasks, such as grooming and sensing their environment.
Habitat Preferences
Burrowing spiders thrive in specific habitats, primarily preferring loose, sandy soils that facilitate digging. They create vertical burrows, which serve as both a home and a hunting ground. These burrows can vary in depth and structure, depending on the species and environmental conditions.
Of the approximately 75 species of Geolycosa worldwide, 18 are found in North America, particularly north of the Rio Grande. This geographical distribution highlights their adaptability to different environments while maintaining their burrowing lifestyle.
Behavior and Lifestyle
Burrowing spiders exhibit a range of behaviors that are closely tied to their underground existence. They are often referred to as "stay-at-homes" because the spiderlings tend to remain close to the maternal burrow after hatching. This behavior increases their chances of survival, as they benefit from the protection offered by their mother and the burrow itself.
When hunting, burrowing spiders use their burrows strategically. They will brace themselves within the tunnel, waiting for unsuspecting prey to approach. Once a potential meal is within reach, they can quickly emerge to capture it using their powerful chelicerae.
Conclusion
Burrowing spiders, particularly those in the genus Geolycosa, are remarkable examples of adaptation in the arachnid world. Their unique burrowing behavior, coupled with their physical characteristics, allows them to thrive in specific habitats. Understanding these spiders not only enhances our knowledge of biodiversity but also highlights the intricate relationships within ecosystems.
Further Exploration
For those interested in observing burrowing spiders, it is essential to approach them with caution and respect. Their burrows can often be found in sandy areas, and observing their behavior can provide valuable insights into their ecological roles.
















 Electromagnetism Pioneer
Electromagnetism Pioneer 
 Health
Health  Fitness
Fitness  Lifestyle
Lifestyle  Tech
Tech  Travel
Travel  Food
Food  Education
Education  Parenting
Parenting  Career & Work
Career & Work  Hobbies
Hobbies  Wellness
Wellness  Beauty
Beauty  Cars
Cars  Art
Art  Science
Science  Culture
Culture  Books
Books  Music
Music  Movies
Movies  Gaming
Gaming  Sports
Sports  Nature
Nature  Home & Garden
Home & Garden  Business & Finance
Business & Finance  Relationships
Relationships  Pets
Pets  Shopping
Shopping  Mindset & Inspiration
Mindset & Inspiration  Environment
Environment  Gadgets
Gadgets  Politics
Politics 