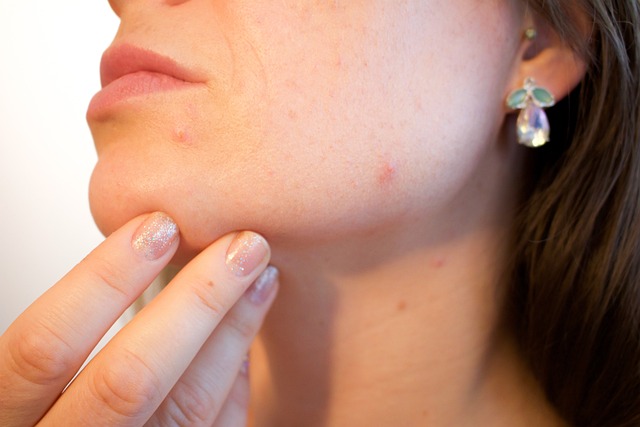
Eczema Rash
Understanding Eczema Rash
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is a prevalent skin condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. Characterized by dry, itchy, and inflamed skin, eczema can manifest in various forms and can significantly impact the quality of life for those affected. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of eczema rash, including its types, symptoms, causes, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Types of Eczema
There are several types of eczema, each with distinct characteristics:
- Atopic Dermatitis: The most common form, often beginning in childhood, characterized by dry, itchy patches that can become inflamed.
- Contact Dermatitis: Caused by direct contact with irritants or allergens, leading to localized rashes.
- Dyshidrotic Eczema: Characterized by small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet, often triggered by stress or exposure to water.
- Nummular Eczema: Presents as circular, coin-shaped patches of irritated skin, often exacerbated by dry skin.
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: Commonly affects oily areas of the body, such as the scalp and face, leading to red, scaly patches.
Symptoms of Eczema
The symptoms of eczema can vary widely among individuals but typically include:
- Itching: Often severe, itching can lead to scratching, which may worsen the condition.
- Dry Skin: Affected areas may appear dry and flaky.
- Red or Brownish-Gray Patches: These patches can appear on various parts of the body, including the hands, feet, ankles, wrists, neck, upper chest, eyelids, and inside the bend of the elbows and knees.
- Thickened, Cracked Skin: Chronic scratching can lead to thickened skin.
- Small, Raised Bumps: These may leak fluid and crust over when scratched.
Causes of Eczema
The exact cause of eczema remains unclear, but it is believed to result from a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Individuals with a family history of eczema, allergies, or asthma are at a higher risk. Common triggers include:
- Environmental allergens (pollen, dust mites, pet dander)
- Irritants (soaps, detergents, fabrics)
- Weather conditions (extreme temperatures, humidity)
- Stress
- Hormonal changes
Diagnosis of Eczema
Diagnosing eczema typically involves a thorough medical history and physical examination by a healthcare professional. In some cases, allergy testing may be conducted to identify specific triggers. It is essential to differentiate eczema from other skin conditions, such as psoriasis or fungal infections, to ensure appropriate treatment.
Treatment Options for Eczema
While there is no cure for eczema, various treatment options can help manage symptoms and reduce flare-ups:
- Moisturizers: Regular application of emollients can help maintain skin hydration and prevent dryness.
- Topical Corticosteroids: These anti-inflammatory medications can reduce redness and itching during flare-ups.
- Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors: Non-steroidal medications that help reduce inflammation and itching.
- Antihistamines: These can alleviate itching, especially at night.
- Phototherapy: Controlled exposure to ultraviolet light can be beneficial for severe cases.
- Systemic Medications: In cases of severe eczema, oral or injectable medications may be prescribed to control inflammation.
Managing Eczema
In addition to medical treatments, individuals with eczema can adopt lifestyle changes to help manage their condition:
- Identify and avoid triggers, such as certain fabrics or environmental allergens.
- Maintain a consistent skincare routine, including regular moisturizing.
- Wear breathable, loose-fitting clothing to minimize irritation.
- Practice stress-reduction techniques, such as mindfulness or yoga.
- Keep nails trimmed to reduce the risk of skin damage from scratching.
When to Seek Professional Help
It is advisable to consult a healthcare professional if eczema symptoms are severe, persistent, or worsening despite treatment. A dermatologist can provide specialized care and may recommend advanced therapies tailored to individual needs.
Conclusion
Eczema is a complex skin condition that requires a multifaceted approach for effective management. By understanding its types, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to alleviate discomfort and improve their quality of life. With appropriate care and lifestyle adjustments, many people with eczema can lead fulfilling lives.
















 Meet Valeria and Camila: The Dynamic Duo
Meet Valeria and Camila: The Dynamic Duo 
 Health
Health  Fitness
Fitness  Lifestyle
Lifestyle  Tech
Tech  Travel
Travel  Food
Food  Education
Education  Parenting
Parenting  Career & Work
Career & Work  Hobbies
Hobbies  Wellness
Wellness  Beauty
Beauty  Cars
Cars  Art
Art  Science
Science  Culture
Culture  Books
Books  Music
Music  Movies
Movies  Gaming
Gaming  Sports
Sports  Nature
Nature  Home & Garden
Home & Garden  Business & Finance
Business & Finance  Relationships
Relationships  Pets
Pets  Shopping
Shopping  Mindset & Inspiration
Mindset & Inspiration  Environment
Environment  Gadgets
Gadgets  Politics
Politics 