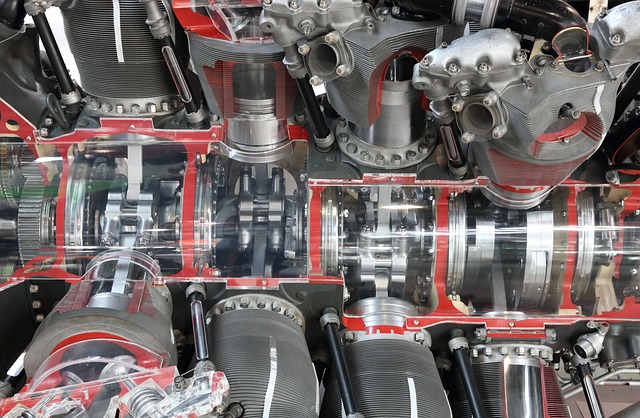
Piston Engines Vs Turboprop
Introduction
In the world of aviation, the choice of engine type can significantly impact performance, cost, and operational capabilities. Two common engine types are piston engines and turboprop engines. Each has its unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different flying needs. This article will explore the characteristics of both engine types to help pilots and aviation enthusiasts understand their options better.
Piston Engines
Piston engines are often regarded as the more traditional choice for general aviation. They operate similarly to car engines, using pistons to convert fuel into mechanical energy. Here are some key features:
- Cost-Effectiveness: Piston-engine aircraft generally have lower purchase prices and operating costs compared to turboprops. This affordability makes them popular among flight schools and casual pilots.
- Fuel Availability: They typically run on aviation gasoline, which is widely available at many airports, making refueling convenient.
- Performance: While piston engines are suitable for shorter flights and lower altitudes, they may struggle with efficiency and speed over long distances.
- Examples: Iconic aircraft such as the P-51 Mustang and Supermarine Spitfire showcase the capabilities of piston engines, particularly in historical contexts.
Turboprop Engines
Turboprop engines represent a more modern approach to aviation propulsion. They combine elements of jet engines and propeller systems, making them versatile for various applications. Key aspects include:
- Efficiency: Turboprop engines are known for their fuel efficiency, especially at higher altitudes and longer distances, making them ideal for regional flights.
- Speed: They offer better speed compared to piston engines, allowing for quicker travel times on longer routes.
- Short-Runway Capability: One of the significant advantages of turboprops is their ability to operate from shorter runways, which is beneficial for accessing remote airports.
- Commercial Use: Turboprop engines are often favored in commercial aviation, where efficiency and speed are crucial for profitability.
Comparative Analysis
When deciding between piston and turboprop engines, several factors should be considered:
- Budget: Piston engines are generally more affordable, making them suitable for private pilots and flight schools. Turboprops, while more expensive, can offer better long-term value for commercial operations.
- Flight Profile: For short, leisurely flights, piston engines are often sufficient. However, for longer distances or higher altitudes, turboprops provide significant advantages.
- Operational Flexibility: Turboprops can operate in diverse environments, including shorter runways, which can be a deciding factor for certain missions.
- Maintenance: Piston engines may require more frequent maintenance due to their mechanical complexity, while turboprops, though more complex, can be more reliable over time.
Conclusion
The choice between piston and turboprop engines ultimately depends on the specific needs of the pilot and the intended use of the aircraft. Piston engines offer a straightforward, cost-effective solution for general aviation, while turboprops provide enhanced performance and efficiency for longer, more demanding flights. Understanding these differences can help pilots make informed decisions that align with their flying goals.















 Camila Mendoza Olmos
Camila Mendoza Olmos 
 Health
Health  Fitness
Fitness  Lifestyle
Lifestyle  Tech
Tech  Travel
Travel  Food
Food  Education
Education  Parenting
Parenting  Career & Work
Career & Work  Hobbies
Hobbies  Wellness
Wellness  Beauty
Beauty  Cars
Cars  Art
Art  Science
Science  Culture
Culture  Books
Books  Music
Music  Movies
Movies  Gaming
Gaming  Sports
Sports  Nature
Nature  Home & Garden
Home & Garden  Business & Finance
Business & Finance  Relationships
Relationships  Pets
Pets  Shopping
Shopping  Mindset & Inspiration
Mindset & Inspiration  Environment
Environment  Gadgets
Gadgets  Politics
Politics 